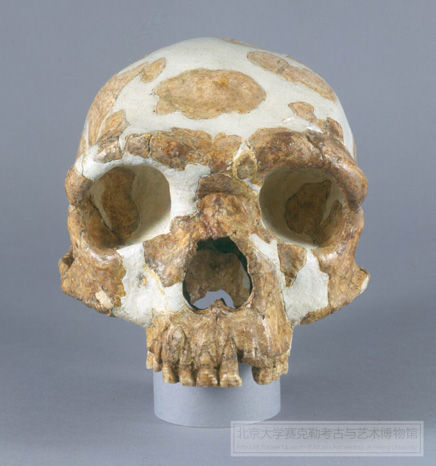
金牛山人頭骨
舊石器時代早期
長20.4,寬14.9厘米
1984年10月2日北京大學考古系在遼寧省營口縣金牛山發掘出土
1984年9月27日至10月6日,在遼寧省營口縣金牛山A地點的洞穴堆積中,發現了一批人類化石。其中有較完整的頭骨(缺下頜)、脊椎骨、肋骨、尺骨、髖骨、髕骨、手骨和足骨等共50余件,屬一青年男性個體。金牛山人的頭骨既保留部份直立人的原始性質,又帶有某些進步特徵,代表了從直立人向早期智人過渡的中間類型。根據下部堆積的地層和共存的動物化石,其地質年代為中更新世晚期。鈾系法年代测定,距今約28,000年。
Frontal View of Skull of Jinniushan Man
Lower
Paleolithic Period
Length:
20.4 cm width: 14.9 cm
Jinniushan,
Yingkou County, Liaoning Province
Excavated October 2, 1984. Department of
Archaeology, Peking University
The
Jinniushan Man fossils were uncovered between September 27 and October 6, 1984 in stratified cave deposits at location A of Jinniushan, near Xidiantun Village, in Yingkou County, Liaoning province. More than fifty fossils found there include a complete skull cap, a backbone, ribs, an ulna, a patella, a hip bone and bones from hands and feet. All of the remains belong to a single young adult male. The fact that the skull cap of Jinniushan Man retains a little of the primitive qualities of Homo erectus but also exhibits some progressive traits suggests that Jinniushan Man is a hominid type that falls between Homo erectus and early Homo sapiens. Based upon an analysis of the stratigraphy and the associated fauna, the date of the fossils is the late Middle Pleistocene. Uranium series testing produced a date of 280,000 years ago.
旧石器时代早期
长20.4,宽14.9厘米
1984年10月2日北京大学考古系在辽宁省营口县金牛山发掘出土
 Arthur M. Sackler Museum of Art and Archaeology at Peking University
Arthur M. Sackler Museum of Art and Archaeology at Peking University